Senasic cutting-edge technology: Tire Safety Monitoring for Safe Driving — High-Integration Bluetooth Tire Pressure Monitoring Chip SNP736
TPMS stands for "Tire Pressure Monitoring System," which is used to monitor blind spots in driving by monitoring tire pressure and temperature. TPMS, along with airbags and ABS systems, forms the three major safety systems in automobiles.
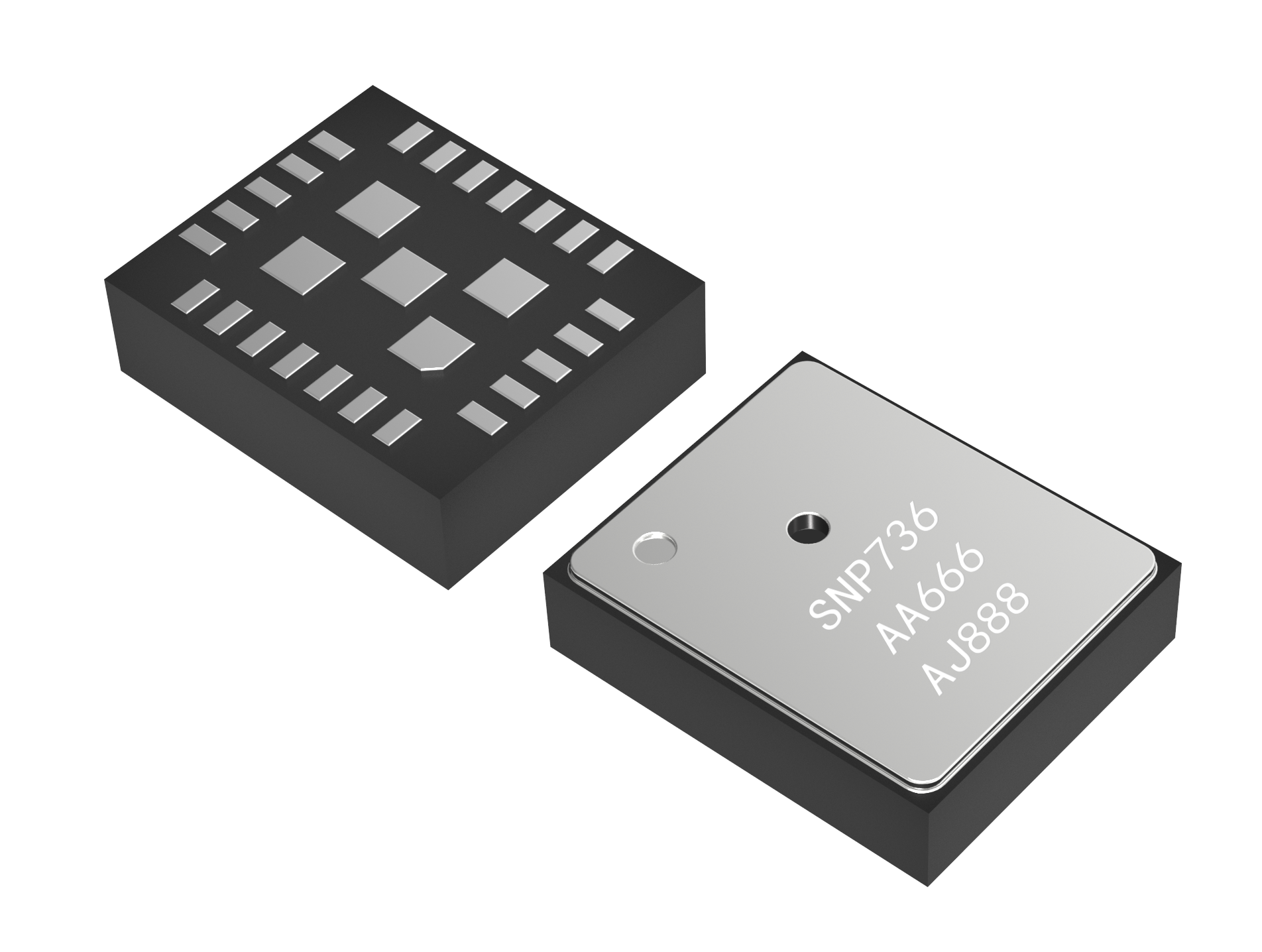
SNP736 is a high-integration Bluetooth tire pressure monitoring chip with BLE transmission functionality. It features high integration, high precision, high reliability, compact size, and low power consumption, making it highly suitable for deployment in new automotive system architectures. It is also suitable for long-distance transmission or transmission scenarios with complex interference sources.
Background Introduction
With the integration and platformization of automotive electrical architectures (EEA), TPMS is also evolving towards integration with intelligent networking and autonomous driving. Low-energy Bluetooth (BLE), with its high stability, low cost, easy deployment, and convenient connection to terminal devices (such as smartphones and tablets), has gradually become one of the mainstream technical solutions for TPMS.
BLE,Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a new, low-power version of Bluetooth technology specifications introduced since Bluetooth 4.0. BLE uses the same 2.4GHz radio frequency as classic Bluetooth, and SNP736 is currently compatible with version 4.2. Its typical features include:
Low Power Consumption: Can run for months to years on button cell batteries.
High Adaptability: Uses the ADV method, which can simultaneously support various BLE devices for viewing.
Long Distance: Strong signal penetration, suitable for long-distance transmission.
High Reliability: Strong anti-interference capability, stable and reliable signal, and frequency-hopping transmission.
Wide Compatibility: Compatible with most existing smartphones, tablets, and computers.
Other features: Small size, low cost, etc.
Working principal
The SNP736 chip allows for customizable programming to control the measurement cycles of pressure, temperature, and battery voltage. Additionally, it enables encoding and encryption of measurement data packets. These encoded and encrypted data packets can then be transmitted via Bluetooth to the receiving end.
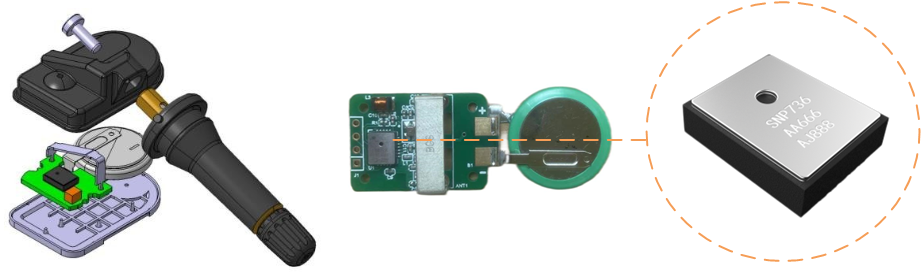
The data transmitted by the sensor via Bluetooth is synchronously received by the onboard central control unit and the mobile phone application. The terminal display device then shows tire-related data (pressure, temperature, etc.) on the screen. In case of abnormal situations such as high or low tire pressure, the terminal will display anomalous data and issue an alert to ensure driving safety.
The diagram below illustrates a TPMS integrated solution with onboard multimedia navigation. Compared to traditional Sub 1G solutions, the peripheral components required for the receiving end are significantly reduced. Since the onboard central control unit itself has built-in Bluetooth receiving functionality, it can replace the receiving module in the solution, thereby achieving cost savings, reduced power consumption, and lightweight design.
Application Scenarios
Compared to traditional Sub 1G applications, the advantages of BLE TPMS mainly lie in not requiring a separate receiver. Instead, it can utilize the vehicle's onboard Bluetooth receiving device, which significantly saves deployment costs. Users can also view tire data at any time through terminal devices such as smartphones and tablets, helping them understand the vehicle's condition in advance and enhancing the user experience.
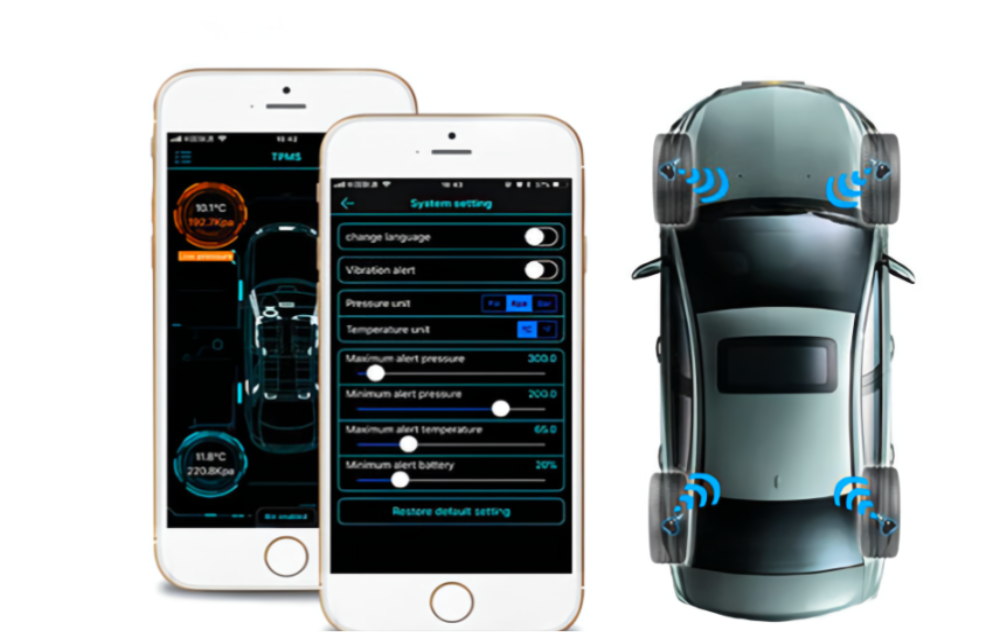
BLE TPMS is also more suitable for deployment in new automotive system architectures. BLE enables TPMS to integrate deeply into intelligent connected vehicle systems, perfectly aligning with the design philosophy of efficient transmission, high integration, small size, lightweight, and intelligent user experience under the innovation of electronic and electrical architectures.

Additionally, BLE TPMS is also well-suited for multi-connected scenarios such as two-wheeled electric vehicles.

System diagram
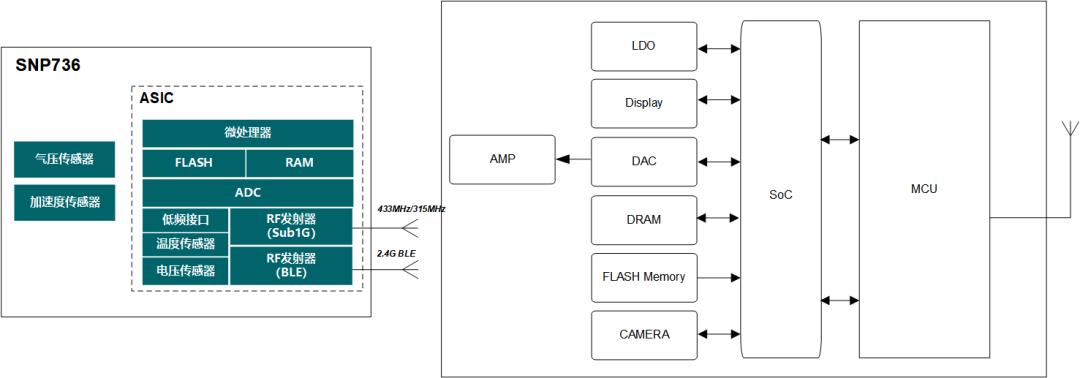
The SNP736 high-integration Bluetooth tire pressure monitoring chip integrates several modules internally, including an 8051 MCU, 12-bit ADC, pressure MEMS, acceleration MEMS, high-frequency (RF) transmitter, and low-frequency (LF) receiver, as illustrated in the diagram below:
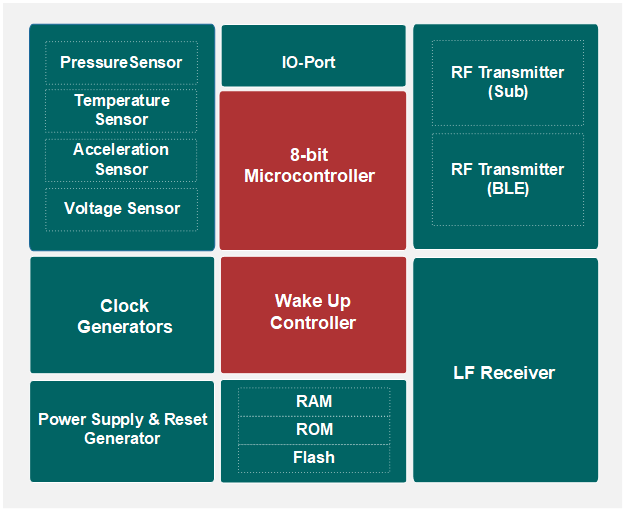
Core Advantages
Features
RF frequency: 433MHz/315MHz/2.4GHz
Modulation: FSK/ASK/GFSK
Measurement range: 900/1900kPa
Quiescent current(3V,25°C): 0.5μA
RF current(2.4GHz,0dBm): 13mA
RF current(433/315MHz,5dBm): 5.2~5.8mA
Operating temperature: -40~125°C
Pressure accuracy(-40~125°C): ±3kPa
Temperature accuracy(-20~70°C): ±2°C
Package: LGA 24pins. 6.0mm x 5.0mm x 1.9mm
For more product information and inquiries about supporting development tools, please contact SENASIC technical support at info@senasic.com.
*Some images are sourced from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.







